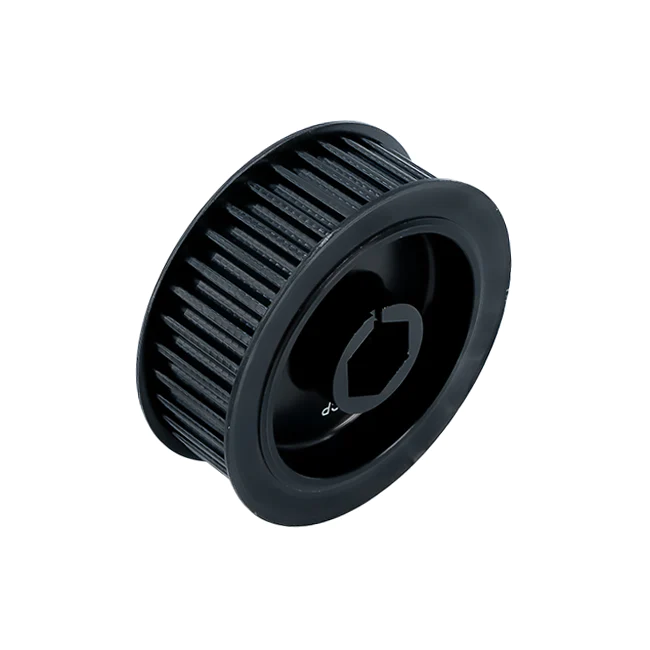
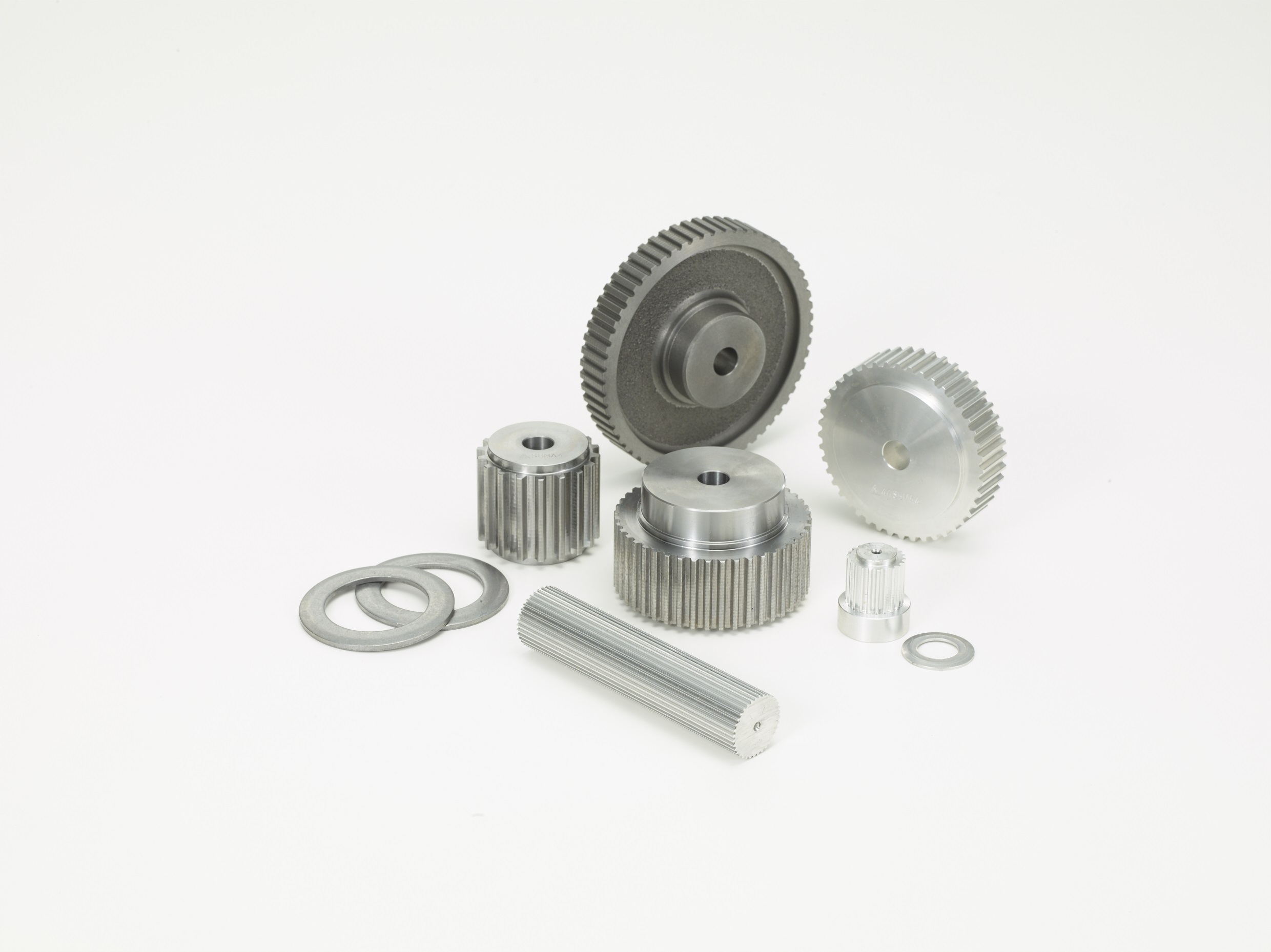
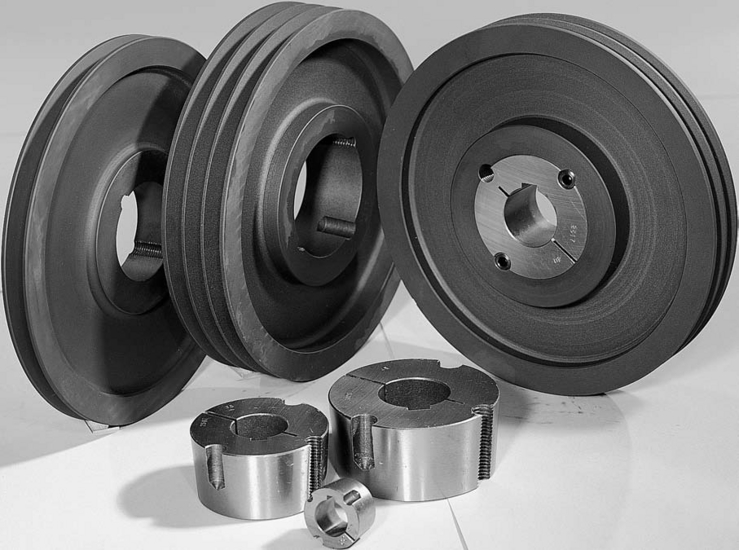
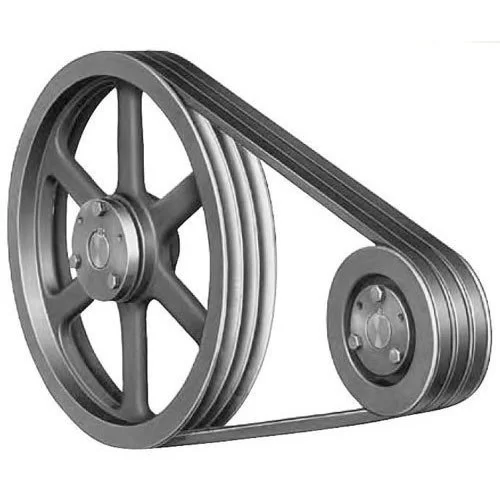
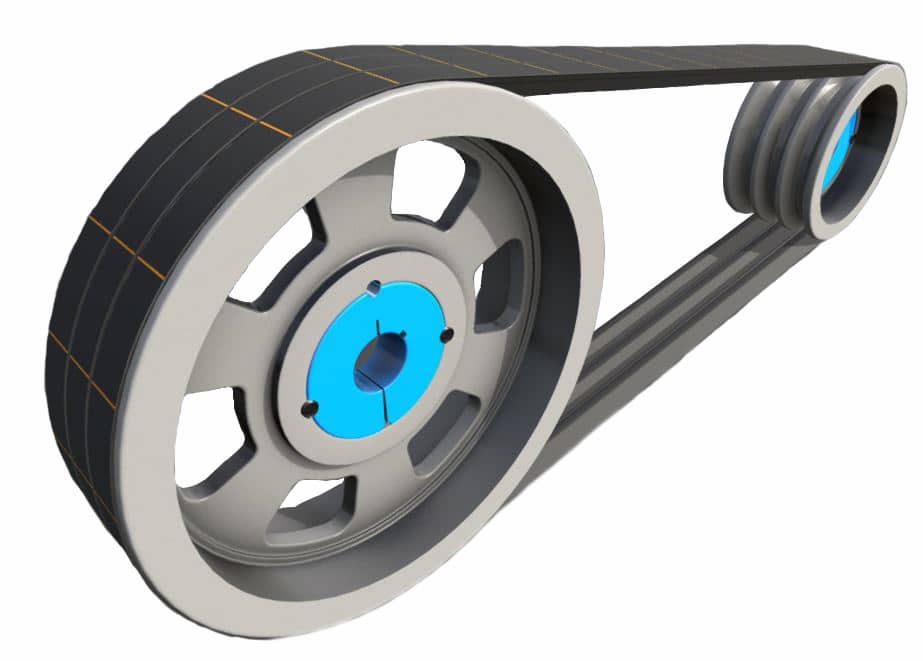
Product Description
Brand: E&B CHINAMFG
| Place of Origin: | HangZhou HangZhou (Mainland) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Model: | MXL XL L H XH XXH T2.5 T5 T10 T20 AT5 AT10 AT20 3M 5M 8M 14M 20M S2M S3M S4.5M S5M S8M S14M P5M P8M P14M etc and other special models | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Material: | Stainless Steel, Brass/Copper, Aluminum, POM, and other standard machineable material. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Module: | 7-160mm, Max.Diameter:14 Mobile: 155718571 http://cxhxbelt /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
Can timing pulleys be used in both simple and complex machinery?Yes, timing pulleys can be used in both simple and complex machinery. Here’s an explanation: Timing pulleys are versatile components that are widely utilized in a range of mechanical systems, irrespective of their complexity. Whether the machinery is simple or complex, timing pulleys offer several advantages that make them suitable for various applications. In Simple Machinery: Timing pulleys are commonly found in simple machinery where the power transmission requirements are relatively straightforward. For example, in small appliances such as electric fans or hand drills, timing pulleys can be used to transfer power from the motor to the rotating components. The simple design and ease of installation make timing pulleys a convenient choice for these types of applications. In Complex Machinery: Timing pulleys also find extensive use in complex machinery where multiple components need to be synchronized and powered efficiently. In industries such as automotive, robotics, printing, packaging, and manufacturing, complex machinery often relies on timing pulley systems to achieve precise coordination and power distribution. The versatility of timing pulleys lies in their ability to handle various power transmission requirements. They can transmit power over long distances, accommodate different torque loads, and operate at high speeds. Timing pulley systems can be configured with different gear ratios by selecting pulleys of varying sizes, enabling customization based on the specific needs of the machinery. Moreover, timing pulleys can be combined with other mechanical components such as tensioners, idler pulleys, and gears to optimize the performance of the machinery. These additional components help maintain proper tension, increase or decrease rotational speed, and ensure smooth operation. Whether the machinery is simple or complex, timing pulleys offer benefits such as accurate timing, reliable power transmission, load distribution, and reduced wear and friction. These advantages contribute to the overall efficiency, performance, and longevity of the machinery. In summary, timing pulleys are versatile components that can be used in both simple and complex machinery. Their flexibility, reliability, and ability to handle various power transmission requirements make them a valuable choice across a wide range of applications.
How do timing pulleys contribute to precision and accuracy in machinery?Timing pulleys play a significant role in enhancing precision and accuracy in machinery. Here’s an explanation of how timing pulleys contribute to precision and accuracy: 1. Synchronization of Components: Timing pulleys ensure precise synchronization of different components in a machinery system. By using toothed timing belts or chains that mesh with the teeth on the pulleys, rotational motion can be accurately transferred from one pulley to another. This synchronization is vital for applications where precise coordination is essential, such as in robotics, printing presses, and conveyor systems. 2. Accurate Timing: Timing pulleys, in combination with timing belts or chains, enable precise timing of operations in machinery. The teeth on the belt or chain engage with the teeth on the pulley, allowing for accurate positioning and control of the driven components. This accuracy in timing ensures that specific actions or tasks occur at the desired intervals, resulting in precise operation and improved overall performance. 3. Consistent Speed and Motion: Timing pulleys contribute to maintaining consistent speed and motion in machinery. The teeth on the timing belt or chain engage with the teeth on the pulley, preventing slippage and maintaining a constant speed ratio between the driving and driven pulleys. This consistency in speed and motion is crucial for applications that require uniform movement, such as in CNC machines or automated assembly lines. 4. Reduced Backlash: Timing pulleys help minimize backlash, which refers to the slight movement or play that can occur when there is a change in the direction of motion. The positive engagement between the teeth on the timing belt or chain and the pulley teeth reduces backlash, ensuring that there is minimal or no lost motion. This reduction in backlash contributes to improved precision and accuracy in the machinery. 5. Repeatable Performance: Timing pulleys enable repeatable performance in machinery. The precise engagement between the teeth on the belt or chain and the pulley ensures that the same motion or action is replicated consistently. This repeatability is essential in applications that require consistent and accurate results, such as in automated manufacturing processes or precision measuring equipment. 6. Tolerance for High Loads: Timing pulleys are designed to handle high loads while maintaining precision and accuracy. The toothed design and robust construction of timing pulleys allow them to transmit power effectively, even under heavy loads. This capability to withstand high loads without compromising precision ensures reliable performance in demanding applications. 7. Compatibility with Automation and Control Systems: The precise and accurate nature of timing pulleys makes them compatible with automation and control systems. They can be easily integrated into computerized control systems, allowing for precise positioning and control of machinery components. This integration enhances the overall precision and accuracy of the system. In summary, timing pulleys contribute to precision and accuracy in machinery by enabling synchronization of components, accurate timing, consistent speed and motion, reduced backlash, repeatable performance, tolerance for high loads, and compatibility with automation and control systems. These characteristics make timing pulleys a fundamental component in achieving precise and accurate operation in various mechanical systems.
What advantages do timing pulleys offer for precise power transmission?Timing pulleys offer several advantages for precise power transmission in mechanical systems. Here are some of the key advantages: 1. Positive Drive System: Timing pulleys, when used in conjunction with a timing belt, create a positive drive system. The teeth on the timing pulleys mesh with the teeth on the timing belt, ensuring a positive engagement and eliminating slippage. This positive drive system enables precise power transmission without loss of motion or power. 2. Accurate Speed Ratios: Timing pulleys allow for accurate speed ratios between the driving and driven components. The number of teeth on the pulleys and the belt determines the speed ratio, ensuring a consistent and predictable transmission of rotational motion. This is crucial in applications where precise speed control and synchronization are required. 3. High Torque Transmission: The positive engagement between the teeth of the timing pulleys and belt allows for efficient transmission of high torque. The teeth effectively transmit the rotational force without slipping or losing power, enabling reliable torque transfer in applications that require high torque output. 4. Precise Positioning and Indexing: Timing pulleys facilitate precise positioning and indexing of components in a mechanical system. The teeth on the pulleys and belt ensure accurate movement and control, allowing for repeatable and controlled motion. This is essential in applications that require precise positioning, such as CNC machines, robotics, and automated systems. 5. Minimal Backlash: The positive engagement between the teeth of timing pulleys results in minimal backlash or play in the power transmission system. Backlash refers to the undesired motion or gap between mating components when the direction of force is reversed. A timing pulley system with minimal backlash ensures precise and immediate response to changes in direction, enhancing overall system performance and accuracy. 6. Reduced Maintenance: Timing pulleys and belts require minimal maintenance compared to other power transmission systems. The positive drive system eliminates the need for frequent tension adjustments and lubrication. Additionally, timing belts made of durable materials with reinforcing cords provide long service life and resist wear, reducing the need for frequent replacements. 7. Low Noise and Vibration: Timing pulleys contribute to low noise and vibration levels in a mechanical system. The positive engagement between the teeth minimizes vibration and noise generation during power transmission. This is especially important in applications where noise and vibration can affect system performance, precision, or user comfort. 8. Design Flexibility: Timing pulleys offer design flexibility, allowing for various configurations and customization options. They are available in different sizes, materials, and tooth profiles to suit specific application requirements. This flexibility enables engineers to design systems that meet precise power transmission needs. Overall, timing pulleys provide significant advantages for precise power transmission, including a positive drive system, accurate speed ratios, high torque transmission, precise positioning, minimal backlash, reduced maintenance, low noise and vibration, and design flexibility. These advantages make timing pulleys a preferred choice in applications where precise motion control, accurate timing, and reliable power transmission are essential.
2024-05-16 China Professional Agricultural Synchronous Aluminum Timing Spinning Taper Lock Bush Idler Flat Poly Grooved Sheave Wheel Adjustable Crankshaft Alternator Tension V Belt Pulley engine pulleyProduct Description
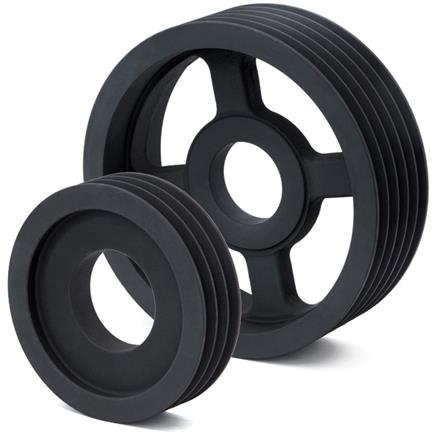
Agricultural Synchronous Aluminum Timing Spinning Taper Lock Bush Idler Flat Poly Grooved Sheave Wheel Adjustable Crankshaft Alternator Tension V Belt Pulley Product Description Pulleys belonging to wheel hub components are generally large in size, and their manufacturing processes are mainly casting and forging. Generally, the design with large size is cast iron (good casting performance), and cast steel is rarely used (poor casting performance); Generally, the smaller size can be designed as forgings and the material is steel. Belt pulley is mainly used for long-distance power transmission, such as the output of small diesel engines, agricultural vehicles, tractors, automobiles, mining machinery, mechanical processing equipment, textile machinery, packaging machinery, lathes, forging machines, power transmission of some small horsepower motorcycles, power transmission of agricultural machinery, air compressors, reducers, reducers, generators, cotton ginners, etc. V-Belt Pulley: The specifications of V-belts are divided by the dimensions of back width (top width) and height (thickness). According to different dimensions of back width (top width) and height (thickness), V-belts of different standards have different models. The pitch width, top width and height of V-belts of each model are different, so the pulley must also make various groove types according to the shape of V-belts; These different groove types determine various types of pulley.
Timing pulley: Spinning is to fix the flat or hollow blank on the mold of the spinning machine. When the blank rotates with the main shaft of the machine, the blank is pressurized with a roller or driving rod to produce local plastic deformation. Spinning is a special forming method. Bore type: pilot bore, finished bore, taper bore, bore for QD bushing.
Related products
Company Profile Production process Certificates /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
What are the maintenance requirements for belt pulleys in industrial settings?In industrial settings, proper maintenance of belt pulleys is essential to ensure their optimal performance, longevity, and safe operation. Here’s a detailed explanation of the maintenance requirements for belt pulleys in industrial settings: 1. Regular Inspection: Belt pulleys should be inspected regularly to identify any signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Inspect the pulleys for cracks, corrosion, excessive wear on the grooves, or any other visible abnormalities. Check for proper alignment by examining the position of the pulleys relative to each other and their corresponding belts. Regular inspections help detect issues early on and prevent further damage or failures. 2. Lubrication: Proper lubrication is crucial for the smooth operation of belt pulleys. Lubricate the pulley bearings according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. This helps reduce friction, heat generation, and wear on the bearings. Use the appropriate lubricant and follow the recommended lubrication intervals to ensure optimal performance and extend the life of the pulleys. 3. Tension Adjustment: Maintaining proper belt tension is vital for the efficient and reliable operation of belt pulleys. Check the tension of the belts regularly using the manufacturer’s guidelines or recommended tensioning devices. Adjust the tension as needed to ensure the belts are neither too loose nor too tight. Proper tensioning allows for effective power transmission, minimizes belt slippage, and reduces wear on the belts and pulleys. 4. Belt Replacement: Over time, belts may wear out or become damaged. Regularly inspect the belts for signs of wear, cracking, fraying, or excessive stretching. If any of these issues are present, replace the belts promptly with new ones of the correct size and type. Using worn or damaged belts can lead to reduced performance, increased risk of pulley damage, and potential system failures. 5. Cleaning: Keep the belt pulleys clean and free from debris, dust, and dirt that may accumulate over time. Use appropriate cleaning methods, such as brushing or compressed air, to remove any contaminants that could affect the pulley’s performance or the grip of the belts. Clean pulleys contribute to better belt traction, reduce the risk of slippage, and improve overall system efficiency. 6. Alignment Correction: Proper pulley alignment is crucial for efficient power transmission and to prevent premature wear. If misalignment is detected during inspections or if the belts are not running smoothly, take corrective measures to align the pulleys correctly. Use alignment tools, such as laser alignment devices, to ensure precise alignment of the pulleys. Proper alignment minimizes belt wear, reduces noise and vibration, and extends the life of the pulleys and belts. 7. Safety Measures: When performing maintenance on belt pulleys, always adhere to safety procedures. Follow lockout/tagout protocols to isolate the equipment from power sources before inspecting or working on the pulleys. Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) to protect against potential hazards. Ensure that maintenance personnel are trained in safe maintenance practices and are familiar with the specific procedures for working with belt pulleys. 8. Record Keeping: Maintain a record of maintenance activities and inspections performed on belt pulleys. This includes dates of inspections, lubrication, tension adjustments, belt replacements, and any corrective actions taken. Keeping a maintenance log helps track the history of maintenance activities, identify recurring issues, and plan future maintenance tasks effectively. In summary, the maintenance requirements for belt pulleys in industrial settings include regular inspections, proper lubrication, tension adjustment, belt replacement, cleaning, alignment correction, adherence to safety measures, and maintaining a maintenance record. By following these maintenance requirements, industrial facilities can ensure the optimal performance, longevity, and safe operation of belt pulleys, contributing to the overall efficiency and reliability of their industrial processes.
Can belt pulleys be customized for specific machinery and equipment?Yes, belt pulleys can be customized to meet the specific requirements of machinery and equipment in various applications. Customization allows for the adaptation of belt pulleys to specific dimensions, performance characteristics, and operational needs. Here’s a detailed explanation of how belt pulleys can be customized for specific machinery and equipment: 1. Dimensional Customization: Belt pulleys can be customized to match the dimensional requirements of the machinery and equipment they will be installed in. This includes customizing the diameter, width, and groove dimensions of the pulleys to ensure proper fit and alignment with the system. Customization ensures that the belt pulleys integrate seamlessly into the machinery, optimizing performance and reliability. 2. Material Selection: Depending on the specific requirements of the machinery and equipment, belt pulleys can be customized with different materials. The choice of materials can be based on factors such as load capacity, environmental conditions, chemical resistance, and operating temperature. Common materials used for customized belt pulleys include steel, aluminum, cast iron, and various composites. Custom material selection ensures that the pulleys can withstand the demands of the application. 3. Specialized Coatings and Finishes: In certain applications, customized belt pulleys may require specialized coatings or finishes to enhance their performance. For example, pulleys used in food processing or pharmaceutical industries may require coatings that comply with specific safety and hygiene standards. Customized coatings can also provide corrosion resistance or reduce friction, improving the overall efficiency and longevity of the pulleys. 4. Groove Profiles: Belt pulleys can be customized with specific groove profiles to match the type of belt being used. Different belts, such as V-belts, timing belts, or flat belts, have varying groove requirements. Customizing the groove profiles ensures optimal belt engagement, maximizing power transmission efficiency and preventing belt slippage. 5. Special Features: In some cases, customized belt pulleys may require additional features or modifications to meet specific operational needs. This can include the incorporation of keyways, set screws, flanges, or other attachments to ensure proper alignment and secure mounting. Customized pulleys can also be designed with specific hub configurations or balancing requirements to achieve smooth and balanced operation in the machinery and equipment. 6. Performance Optimization: Customized belt pulleys can be tailored to optimize performance in specific applications. This may involve adjusting the pulley design, such as modifying the number of grooves or altering the pitch diameter, to achieve the desired speed ratios or torque requirements. Performance optimization ensures that the customized pulleys contribute to the efficient and reliable operation of the machinery and equipment. Overall, belt pulleys can be customized to match the dimensional requirements, material specifications, coating needs, groove profiles, special features, and performance optimization of specific machinery and equipment. Customization ensures that the pulleys seamlessly integrate into the system, providing efficient power transmission and meeting the unique operational needs of the application.
What is a belt pulley, and how is it used in mechanical systems?A belt pulley is a mechanical device used in various systems to transmit power and motion between rotating shafts. It consists of a wheel with a grooved rim, known as the pulley, that is connected to a shaft. The pulley is typically made of materials such as cast iron, steel, or aluminum. It is used in conjunction with a belt or a rope to transfer rotational motion from one shaft to another. Here’s a detailed explanation: A belt pulley is essential in mechanical systems for the following purposes:
In summary, a belt pulley is a mechanical device used for power transmission and motion control in various mechanical systems. It connects rotating shafts through belts or ropes, allowing power to be transmitted from one shaft to another. Belt pulleys provide speed control, directional change, tension control, noise and vibration reduction, as well as compatibility and interchangeability benefits. By utilizing belt pulleys, mechanical systems can efficiently transfer power, control speeds, and enable the operation of different components or systems in desired directions.
2024-04-02 China manufacturer Agricultural Synchronous Aluminum Timing Spinning Taper Lock Bush Idler Flat Poly Grooved Sheave Wheel Adjustable Crankshaft Alternator Tension V Belt Pulley pulley alternatorProduct Description
Agricultural Synchronous Aluminum Timing Spinning Taper Lock Bush Idler Flat Poly Grooved Sheave Wheel Adjustable Crankshaft Alternator Tension V Belt Pulley Product Description Pulleys belonging to wheel hub components are generally large in size, and their manufacturing processes are mainly casting and forging. Generally, the design with large size is cast iron (good casting performance), and cast steel is rarely used (poor casting performance); Generally, the smaller size can be designed as forgings and the material is steel. Belt pulley is mainly used for long-distance power transmission, such as the output of small diesel engines, agricultural vehicles, tractors, automobiles, mining machinery, mechanical processing equipment, textile machinery, packaging machinery, lathes, forging machines, power transmission of some small horsepower motorcycles, power transmission of agricultural machinery, air compressors, reducers, reducers, generators, cotton ginners, etc. V-Belt Pulley: The specifications of V-belts are divided by the dimensions of back width (top width) and height (thickness). According to different dimensions of back width (top width) and height (thickness), V-belts of different standards have different models. The pitch width, top width and height of V-belts of each model are different, so the pulley must also make various groove types according to the shape of V-belts; These different groove types determine various types of pulley.
Timing pulley: Spinning is to fix the flat or hollow blank on the mold of the spinning machine. When the blank rotates with the main shaft of the machine, the blank is pressurized with a roller or driving rod to produce local plastic deformation. Spinning is a special forming method.
Bore type: pilot bore, finished bore, taper bore, bore for QD bushing. Related products
Company Profile Production process Certificates
What is the importance of proper pulley alignment and tensioning in belt pulley systems?Proper pulley alignment and tensioning are of utmost importance in belt pulley systems. They directly impact the efficiency, reliability, and longevity of the system. Here’s a detailed explanation of the importance of proper pulley alignment and tensioning: 1. Power Transmission Efficiency: Proper pulley alignment and tensioning ensure efficient power transmission in belt pulley systems. Misaligned pulleys or incorrect belt tension can lead to slippage, which results in power loss. When the belts slip on the pulleys, the intended power transfer from the driving pulley to the driven pulley is compromised. By aligning the pulleys correctly and maintaining proper tension, the belts grip the pulleys securely, allowing for efficient power transmission and maximizing the system’s overall efficiency. 2. Prevents Belt Wear and Damage: Improper pulley alignment and tensioning can cause excessive belt wear and damage. Misaligned pulleys can cause the belts to run at an angle, resulting in uneven wear on the belt’s edges. This can lead to premature belt failure and the need for frequent belt replacements. Insufficient or excessive belt tension can also cause accelerated wear, as it puts additional strain on the belts. Proper alignment and tensioning help distribute the load evenly across the belts, minimizing wear and extending their lifespan. 3. Reduces Noise and Vibration: Correct pulley alignment and tensioning contribute to reducing noise and vibration in belt pulley systems. Misaligned pulleys can cause the belts to vibrate and generate noise during operation. Excessive belt tension can lead to increased vibration as well. These vibrations and noise not only affect the comfort of operators but can also impact the overall stability and performance of the system. Proper alignment and tensioning help minimize vibration and noise levels, creating a smoother and quieter operation. 4. Improves System Reliability: Proper pulley alignment and tensioning enhance the reliability of belt pulley systems. Misalignment or improper tension can lead to unexpected belt failures, system downtime, and costly repairs. When the belts slip or wear unevenly, it can cause disruptions in power transmission, resulting in reduced system performance or complete failure. Proper alignment and tensioning minimize the risk of belt-related issues, ensuring the system operates reliably and consistently. 5. Enhances Component Life: Correct pulley alignment and tensioning contribute to the longevity of system components. When the belts run smoothly and grip the pulleys properly, it reduces stress on the pulleys, bearings, and other mechanical parts. Misalignment or excessive tension can cause unnecessary strain on these components, leading to premature wear and failure. Proper alignment and tensioning help distribute the load evenly, minimizing stress and extending the life of system components. 6. Facilitates Easy Maintenance: Proper pulley alignment and tensioning make maintenance tasks easier. When pulleys are aligned correctly, it simplifies belt replacement, adjustment, or inspection procedures. Easy access to the belts and pulleys allows for efficient maintenance and reduces downtime during servicing. Additionally, proper tensioning ensures that belts can be adjusted or replaced without difficulty, improving overall serviceability of the system. 7. Optimizes System Performance: Ultimately, proper pulley alignment and tensioning optimize the performance of belt pulley systems. When the belts are aligned correctly and tensioned properly, the power transmission is efficient, wear is minimized, and vibrations are reduced. This results in reliable and consistent system operation, allowing the system to perform at its intended level of efficiency and productivity. In summary, proper pulley alignment and tensioning are essential for efficient power transmission, prevention of belt wear and damage, reduction of noise and vibration, and improvement of system reliability. They enhance the lifespan of system components, facilitate maintenance tasks, and optimize the overall performance of belt pulley systems. By ensuring correct alignment and tension, operators can maximize the efficiency, reliability, and longevity of their belt pulley systems.
Can belt pulleys be customized for specific machinery and equipment?Yes, belt pulleys can be customized to meet the specific requirements of machinery and equipment in various applications. Customization allows for the adaptation of belt pulleys to specific dimensions, performance characteristics, and operational needs. Here’s a detailed explanation of how belt pulleys can be customized for specific machinery and equipment: 1. Dimensional Customization: Belt pulleys can be customized to match the dimensional requirements of the machinery and equipment they will be installed in. This includes customizing the diameter, width, and groove dimensions of the pulleys to ensure proper fit and alignment with the system. Customization ensures that the belt pulleys integrate seamlessly into the machinery, optimizing performance and reliability. 2. Material Selection: Depending on the specific requirements of the machinery and equipment, belt pulleys can be customized with different materials. The choice of materials can be based on factors such as load capacity, environmental conditions, chemical resistance, and operating temperature. Common materials used for customized belt pulleys include steel, aluminum, cast iron, and various composites. Custom material selection ensures that the pulleys can withstand the demands of the application. 3. Specialized Coatings and Finishes: In certain applications, customized belt pulleys may require specialized coatings or finishes to enhance their performance. For example, pulleys used in food processing or pharmaceutical industries may require coatings that comply with specific safety and hygiene standards. Customized coatings can also provide corrosion resistance or reduce friction, improving the overall efficiency and longevity of the pulleys. 4. Groove Profiles: Belt pulleys can be customized with specific groove profiles to match the type of belt being used. Different belts, such as V-belts, timing belts, or flat belts, have varying groove requirements. Customizing the groove profiles ensures optimal belt engagement, maximizing power transmission efficiency and preventing belt slippage. 5. Special Features: In some cases, customized belt pulleys may require additional features or modifications to meet specific operational needs. This can include the incorporation of keyways, set screws, flanges, or other attachments to ensure proper alignment and secure mounting. Customized pulleys can also be designed with specific hub configurations or balancing requirements to achieve smooth and balanced operation in the machinery and equipment. 6. Performance Optimization: Customized belt pulleys can be tailored to optimize performance in specific applications. This may involve adjusting the pulley design, such as modifying the number of grooves or altering the pitch diameter, to achieve the desired speed ratios or torque requirements. Performance optimization ensures that the customized pulleys contribute to the efficient and reliable operation of the machinery and equipment. Overall, belt pulleys can be customized to match the dimensional requirements, material specifications, coating needs, groove profiles, special features, and performance optimization of specific machinery and equipment. Customization ensures that the pulleys seamlessly integrate into the system, providing efficient power transmission and meeting the unique operational needs of the application.
What are the key components and design features of a belt pulley?A belt pulley consists of several key components and incorporates specific design features to ensure efficient power transmission and reliable operation. Understanding these components and design features is essential for proper selection and utilization of belt pulleys in mechanical systems. Here’s an overview of the key components and design features: 1. Pulley Body: The pulley body is the main structure of the belt pulley. It is typically a wheel-shaped component made of materials such as cast iron, steel, or aluminum. The pulley body provides the necessary strength and rigidity to support the belt and transmit rotational motion. 2. Grooved Rim: The rim of the pulley body features a series of grooves or channels. These grooves accommodate the belt or rope, ensuring a secure engagement between the pulley and the transmission element. The groove profile can vary depending on the type of belt or rope being used. 3. Hub or Bore: The hub or bore is the central opening in the pulley body. It allows the pulley to be mounted and secured onto the shaft. The hub may have keyways, splines, or other features to ensure proper alignment and torque transfer between the pulley and the shaft. 4. Flanges: Flanges are raised edges or rims located on the sides of the pulley body, adjacent to the grooved rim. Flanges help guide and prevent the belt from slipping off the pulley during operation. They provide additional support and stability to the belt, ensuring reliable power transmission. 5. Tensioning Mechanism: Some belt pulley designs incorporate a tensioning mechanism. This mechanism allows for adjusting the tension in the belt to ensure proper engagement and prevent slippage. Tensioning mechanisms can include adjustable pulley halves, movable pulley arms, or other mechanisms that enable easy tension adjustment. 6. Idler Pulleys: In certain belt-driven systems, idler pulleys are used in conjunction with the main driving and driven pulleys. Idler pulleys are additional pulleys that do not transmit power but help guide and redirect the belt. They maintain the appropriate tension in the belt, improve belt wrap around the pulleys, and assist in achieving the desired belt path. 7. Surface Finish: The surface finish of a belt pulley is important for reducing friction and wear between the pulley and the belt. Smooth and properly finished surfaces minimize belt slippage and improve power transmission efficiency. The surface finish can be achieved through machining, grinding, or other methods depending on the material and application requirements. 8. Balancing: Balancing is a critical aspect of belt pulley design, especially for high-speed applications. Proper balancing ensures that the pulley rotates smoothly without causing excessive vibrations or premature wear. Unbalanced pulleys can lead to reduced system performance, increased noise, and potential damage to the pulley or other components. 9. Material Selection: The choice of material for a belt pulley depends on factors such as the application requirements, load capacity, operating conditions, and cost considerations. Common materials used for pulleys include cast iron, steel, aluminum, and composite materials. Each material offers specific advantages in terms of strength, durability, corrosion resistance, and weight. In summary, a belt pulley consists of components such as the pulley body, grooved rim, hub or bore, flanges, tensioning mechanisms, and may include idler pulleys. Design features like surface finish, balancing, and material selection are crucial for optimal performance and longevity of the pulley. Understanding these key components and design features allows for the appropriate selection, installation, and maintenance of belt pulleys in mechanical systems.
2023-09-22 china factory Taper Lock Timing Belt Pulley High Quality Manufactory Euro Standard manufacturers
Merchandise Description
Item Description Complex Profile:
Requirements:
Basic Data:
Select Shaft Bore Diameter:
[ ! ]Electroless nickel plated bushing decreases highest allowable torque and allowable thrust load by 20~30% Rewards: Software: Relevant image: Organization Profile Packaging & CZPT Shipping and delivery : DHL, EMS, Air mail,TNT,UPS and FedEx.
ep has a extensive assortment of pulleys in inventory and all set to ship. All spare pulleys are produced of higher-quality aluminum and have pilot holes as normal. Flanges are manufactured of metal zinc sheet if needed, but you can specify other resources by custom made purchase. Inventory aluminum pulleys are accessible in imperial and metric pitches. We can modify inventory pulleys according to your demands. You can get in touch with customer services for pricing and supply. china best Htd5m-15 72tooth Taper Bore Timing Belt Pulley with 1610 Taper Lock manufacturers
Item Description
Principal Merchandise: Timing belt pulleys, timing bars, timing belt clamping plates. Locking aspects and shrink discs: CZPT substitute for Ringfeder, Sati, Chiaravalli, BEA, KBK, Tollok, and so forth. V belt pulleys and taper lock bush. Sprockets, idler, and plate wheels. Gears and racks: spur equipment, CZPT cal equipment, bevel equipment, CZPT , equipment rack. Shaft couplings: miniature coupling, curved tooth coupling, chain coupling, HRC coupling, NM coupling, FCL coupling, GE coupling, rigid and CZPT , jaw coupling, disc coupling, multi-beam coupling, CZPT joint, torque limiter, shaft collars. Forging, CZPT , Stamping Areas. Advantage: one. Factory right offer , we can carry on to provide a stable offer 10.Kinds of surface treatment—Zinc Plating, Powder Coating, Anodizing, Chrome Plate, RoHs .and so on .
In a dual pulley system, this ratio is equivalent to the reference diameter of the output pulley being better than the reference diameter of the input pulley. It truly is reasonably uncomplicated as extended as you calculate the equipment ratios for a more intricate pulley method step by phase. For several pulleys, the ratios of the a variety of elements of the system should be calculated to establish the overall ratio. In the image above, the reference diameter of the lower travel wheel is 20mm, the radius of the higher wheel is 40mm, and the ratio is 2:1. 2 spins on the reduced wheel and 1 spin on the higher wheel. The equipment ratio also tells us one thing about the torque of the program due to the fact the ratio of output torque to enter torque is equivalent to the equipment ratio. Therefore, the torque applied to the upper wheel is two times as quick, but the speed is halved. china sales Plastic Taper Lock V Belt Nylon Timing Pulley Belt for Transmission China Factory Manufacturer manufacturers
Merchandise Description
Plastic Taper Lock V Belt Nylon Timing Pulley Belt for Transmission CZPT Manufacturing facility CZPT r one) V-Belt pulleys for taper bushes
two)V-belt pulleys with strong hub
3) Adjustable CZPT V-belt pulleys prebored and for taper bushes
Fixed pulleys are pulleys that maintain the drum at one particular level. While the pressure essential to raise or transfer an object is no distinct than lifting it with your arms, stationary pulleys enable you to alter the course of the required power. For illustration, when hooked up to a bucket that draws h2o from a well, a stationary drinking water puller allows you to pull the drinking water sideways, lifting the bucket in a a lot more practical way than pulling it vertically, one particular hand at a time. The fat of the bucket is even now the very same, but it is simpler to carry. china Cheap High Quality Transmission Timing Pulley and Belt with Taper Lock for Machine Manufacturer Industrial manufacturers
Item Description
Large High quality Transmission Timing Pulley and Belt with Taper Lock for CZPT CZPT r CZPT one) V-Belt pulleys for taper bushes
two)V-belt pulleys with strong hub
3) Adjustable CZPT V-belt pulleys prebored and for taper bushes
In a twin pulley method, this ratio is equal to the reference diameter of the output pulley getting increased than the reference diameter of the enter pulley. It really is pretty straightforward as long as you calculate the gear ratios for a much more sophisticated pulley technique action by action. For a number of pulleys, the ratios of the a variety of parts of the mechanism have to be calculated to establish the total ratio. In the photograph previously mentioned, the reference diameter of the lower drive wheel is 20mm, the radius of the upper wheel is 40mm, and the ratio is 2:1. 2 spins on the decrease wheel and 1 spin on the upper wheel. The equipment ratio also tells us something about the torque of the technique because the ratio of output torque to enter torque is equivalent to the equipment ratio. For that reason, the torque utilized to the higher wheel is 2 times as rapidly, but the pace is halved. china Cheap Manufactory Euro Standard Taper Lock Timing Belt Pulley High Quality manufacturers
Item Description
Manufacturer: E&B CZPT
Applicable business: CZPT ctro-equipment, Textile CZPT ry, Advertisement printing equipment, Foodstuff CZPT , CNC device, CZPT ation, tobacco and so on Observe when examining from and order pulley,
Arc tooth Timing tooth
Dimension of T kind/linear kind pulley
Illustration OF PULLEY
Contect Us:
A movable pulley is a pulley where when you go a hefty object, the drum moves with it. There is no change in the path of the force you need to have to utilize, but the load will “really feel” lighter than it really is. For illustration, if you happen to be hauling a large hay bale up the barn’s attic, a moveable pulley will make the load truly feel a great deal lighter, even however you are pulling in the identical route. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||